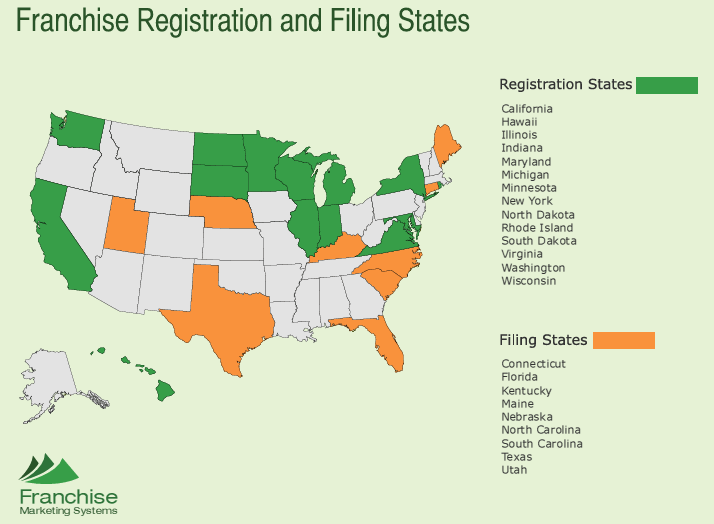
Franchising is a dynamic and regulated business model that requires compliance with state and federal laws to ensure transparency and protection for both franchisors and franchisees. One critical aspect of regulatory compliance is the process of franchise state registrations. This overview delves into the intricacies of franchise state registrations, examining the purpose, key components, and steps involved in navigating this complex regulatory landscape.
I. Understanding Franchise State Registrations:
Franchise state registrations are a legal requirement imposed by individual states to regulate and oversee the sale of franchises within their jurisdiction. These registrations are intended to safeguard prospective franchisees by ensuring that they receive essential information about the franchisor, the franchise offering, and the risks associated with the investment.
Each state has its own set of regulations and requirements governing franchise sales. While some states have specific laws that regulate franchises, others may incorporate franchise regulations within their general business laws. Understanding and complying with these regulations is crucial for franchisors to conduct legal and ethical business operations.
II. Key Components of Franchise State Registrations:
- Franchise Disclosure Document (FDD):The cornerstone of franchise state registrations is the Franchise Disclosure Document (FDD). The FDD is a comprehensive legal document that provides detailed information about the franchisor, the franchise system, and the terms and conditions of the franchise offering. It typically includes 23 specific items, covering everything from the franchisor’s business background to the initial investment required by the franchisee.
- State-Specific Addenda:In addition to the federally mandated FDD, certain states may require franchisors to include state-specific addenda or amendments to address unique regulations or disclosure requirements within that state. These addenda ensure that the franchisor complies with state laws and provides franchisees with relevant information specific to the state in which they are purchasing the franchise.
- Registration Fees:To initiate the franchise state registration process, franchisors are typically required to pay registration fees to each state regulatory authority. These fees vary from state to state and contribute to the cost of administering and overseeing the franchise registration process.
- Renewal Requirements:Franchise state registrations are not static; they may require periodic renewals. Franchisors must stay informed about renewal deadlines and comply with any additional requirements specified by each state to maintain their legal standing.
III. Steps Involved in Franchise State Registrations:
- Preparation of FDD:The process begins with the preparation of the Franchise Disclosure Document. This document requires careful attention to detail and accuracy, as it serves as the primary source of information for prospective franchisees. Franchisors often seek legal counsel with expertise in franchise law to ensure that the FDD complies with federal and state regulations.
- State-Specific Compliance:Franchisors must review each state’s franchise regulations to identify state-specific requirements and ensure compliance. This may involve preparing and filing state-specific addenda, addressing unique disclosure requirements, or modifying certain clauses in the FDD to align with state laws.
- Engagement with Legal Counsel:Given the complex nature of franchise state registrations, engaging with experienced franchise attorneys is crucial. Legal counsel can provide guidance on compliance matters, assist in preparing state-specific addenda, and navigate the nuances of each state’s regulatory framework.
- Filing and Payment of Fees:Once the FDD is prepared and state-specific requirements are addressed, franchisors submit their franchise state registrations to the relevant state regulatory authorities. This process involves completing application forms, paying registration fees, and providing any additional documentation requested by the state.
- State Review and Approval:State regulatory authorities review the submitted documents to ensure compliance with applicable laws. This may involve a thorough examination of the FDD, state-specific addenda, and financial statements. The state may request additional information or clarification during the review process.
- Issuance of Franchise State Registration:Upon successful completion of the review process and satisfaction of all requirements, the state regulatory authority issues a franchise state registration. This registration grants the franchisor the legal authority to offer and sell franchises within that specific state.
- Renewal and Ongoing Compliance:Franchise state registrations are not perpetual. Franchisors must be mindful of renewal deadlines and fulfill any ongoing compliance requirements stipulated by each state. Failure to renew registrations or maintain compliance can result in legal consequences and restrictions on franchise sales within that state.
IV. Challenges and Considerations:
- Varying State Requirements:Each state has its own set of rules and requirements for franchise state registrations. Navigating these variations can be challenging for franchisors, necessitating a thorough understanding of the unique regulatory landscape in each state where they intend to operate.
- Cost Implications:The cost of franchise state registrations can add up quickly, especially for franchisors expanding into multiple states. Franchisors must budget for registration fees, legal fees, and any additional costs associated with compliance to avoid financial strain.
- Timely Compliance:Meeting deadlines for franchise state registrations and renewals is crucial. Failure to comply with regulatory timelines can lead to legal repercussions, including fines and restrictions on franchise sales.
- Monitoring Legal Changes:Franchisors must stay vigilant about changes in state and federal franchise laws. Periodic reviews and updates to the FDD and compliance procedures may be necessary to ensure ongoing adherence to regulatory requirements.
Franchise state registrations are a critical component of the regulatory framework governing the franchising industry. Navigating the complexities of these registrations requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a commitment to compliance. By understanding the key components of franchise state registrations, engaging legal counsel, and staying informed about state-specific requirements, franchisors can ensure that their expansion efforts are conducted legally and ethically, providing a solid foundation for sustainable growth in the competitive world of franchising.
For more information on Franchise State Registrations and the Franchise Registration process when you franchise your business model, visit the FMS Franchise site: https://www.fmsfranchise.com/learn/resources/state-guidelines/
